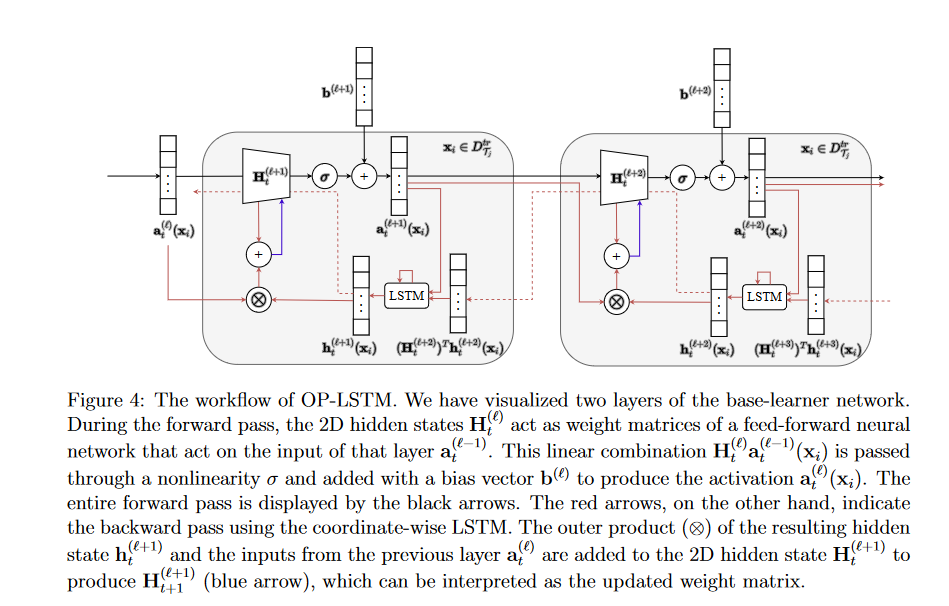
Ilia Sucholutsky, Matthias Schonlau,‘Less Than One’-Shot Learning: Learning N Classes From M<N Samples, In AAAI 2021 Proceedings .
Inspiration
软标签比硬标签携带更多信息,可以适用于LO场景。
- 软标签可以标注样本间的共同特征,进而以这种方式增加信息密度和维度
- 目标:训练样本足够少的情况下,模型还能够以足够的精度识别尽可能多的类别
Terms
prototypes: soft-labelled synthetic images
unrestricted soft label:各个元素可以是任何值,包括负数。
soft\probabilistic label:一个样本在各个类上的概率分布,各个类上的概率之和为1,可以使用softmax函数得到。
hard label:在soft label上使用argmax得到。
soft-label prototype (SLaP):(X,Y),特征向量和它对应的软标签。
Corollary
推论
Work& Finding
hard label prototype Distance-weighted kNN is the special case of SLaPkNN(基于距离度量的软标签原型KNN)
分析这些决策景观,得出使用 M < N 软标签样本分离 N 个类别的理论下限,并研究所得系统的稳健性。
1.分析创建的决策边界鲁棒性和稳定性的方法;
2.软标签表征 训练集用于区分,比起硬标签使用的原型更少。理想情况,是O(N^2)降低到O(1)。
实验
一种有趣的提法
通过描述,我们可以用犀牛 、马两类样本获得除犀牛、马以外 的独角兽的分类。
FSL让模型更加样本有效。
References
都在想办法对数据集进行蒸馏,
1.2019,软标签数据集蒸馏
Sucholutsky, I.; and Schonlau, M. 2019. Soft-Label Dataset Distillation and Text Dataset Distillation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.02551 .
2.2006,动态数据冻结
Ruta, D. 2006. Dynamic data condensation for classification. In International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing, 672–681. Springer.
经典的小样本学习网络结构
1.匹配网络2016:
Vinyals, O.; Blundell, C.; Lillicrap, T.; Wierstra, D.; et al. 2016. Matching networks for one shot learning. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 3630–3638.
2.原型网络,2017
Snell, J.; Swersky, K.; and Zemel, R. 2017. Prototypical networks for few-shot learning. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 4077–4087.
3.李飞飞,小样本识别
Fei-Fei, L.; Fergus, R.; and Perona, P. 2006. One-shot learning of object categories. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 28(4): 594–611.
其他内容
0.1996,借助统计学习模型的主动学习
Cohn, D. A.; Ghahramani, Z.; and Jordan, M. I. 1996. Active learning with statistical models. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research 4: 129–145.
1.2017,卷积神经网络的主动学习方法
Sener, O.; and Savarese, S. 2017. Active learning for convolutional neural networks: A core-set approach. arXiv preprint arXiv:1708.00489 .
2.2005,SVM在大数据集上的快速训练
Tsang, I. W.; Kwok, J. T.; and Cheung, P.-M. 2005. Core vector machines: Fast SVM training on very large data sets. Journal of Machine Learning Research 6(Apr): 363–392.
3.SVM的主动学习2001
Tong, S.; and Koller, D. 2001. Support vector machine active learning with applications to text classification. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2(Nov): 45–66.
4.2008,软标签上的分类对于标签噪声具有鲁棒性。
Thiel, C. 2008. Classification on soft labels is robust against label noise. In International Conference on KnowledgeBased and Intelligent Information and Engineering Systems, 65–73. Springer.
5.2014,KNN的随机邻居压缩
Kusner, M.; Tyree, S.; Weinberger, K.; and Agrawal, K. 2014. Stochastic neighbor compression. In International Conference on Machine Learning, 622–630.